News
마더투베이비의 새로운 소식을 전해드려요.
2024년 추계 모자보건학회 마더세이프 상
페이지 정보
본문
(사)임산부약물정보센터에서는 매해 모자 보건 관련 연구자들을 위한 사업의 일환으로 한국모자보건학회-마더세이프상을 후원하고 하고 있습니다.
2024년 마더세이프상은 아래와 같은 연구 내용이 선정되어 수상 되었음을 알려드립니다.
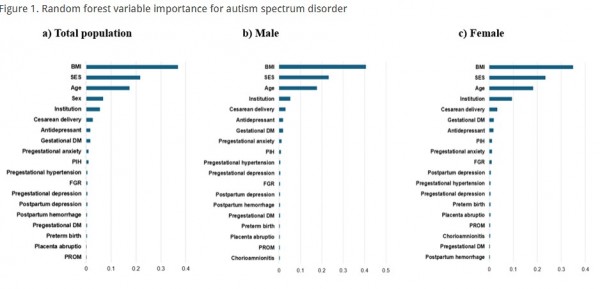
Sex-Based Differences in Prenatal and Perinatal Predictors of Autism Spectrum Disorder using Machine Learning with National Health Data
Objective
This study aimed to develop sex-specific prenatal and perinatal prediction models for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) using machine learning and a national population database.
Methods
A retrospective cohort design was employed, utilizing data from the Korea National Health Insurance Service claims database. The study included 75,105 children born as singletons in 2007 and their mothers, with follow-up data from 2007 to 2021. Twenty prenatal and perinatal risk factors from 2002–2007 were analyzed. Logistic regression and random forest models were used to predict ASD, with performance metrics including accuracy and area under the curve (AUC). Random forest variable importance and SHapley Additive exPlanation (SHAP) values were used to identify major predictors and analyze associations.
Results
The random forest model outperformed logistic regression, with higher accuracy (0.996 vs. 0.686) and AUC (0.997 vs. 0.561). Major predictors included pregestational body mass index (BMI) (0.3679), socioeconomic status (0.2164), maternal age at birth (0.1735), sex (0.0682), and delivery institution (0.0549). SHAP analysis showed that low maternal BMI increased ASD risk in both sexes, while high BMI was associated with greater risk in females. A U-shaped relationship between socioeconomic status and ASD risk was observed, with increased risk in males from lower socioeconomic backgrounds and females from higher ones.
Conclusion
This study identified pregestational BMI, SES, maternal age at birth, sex, and delivery institution as significant predictors of ASD. Maternal pregestational BMI and SES exhibited varying effects on ASD between male and female offspring. Understanding these sex-specific predictors is crucial for enabling prevention, early diagnosis, and intervention strategies tailored to each sex.